
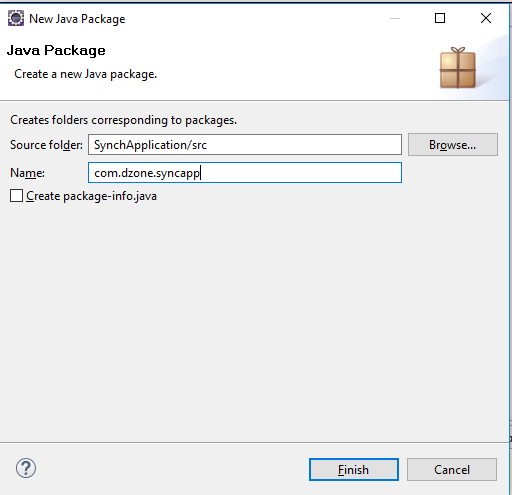
- #File synchronization java install#
- #File synchronization java update#
- #File synchronization java free#
Syncthing doesn’t need to verify ownership to a trusted third party because the trust of the other end is established with this exchange of Device IDs. The Device ID which you need to connect two peers is generated from the public key.
#File synchronization java install#
In the case of Syncthing, it generates a public-private key pair when you install it. The web works this way as it’s not realistic to add certificates of websites manually to the trusted set. You need to verify domain ownership to get a valid certificate from the issuer.

If the website can provide a chain of certificates that can reach a trusted root then the browser will trust this connection. Then another certificate is signed by this trusted one, and so on. There is a chain of trust here where a certificate is signed by a trusted root, so it becomes trusted too. The browser trusts only a few root certificates but not the ones provided by the website. How Syncthing can use TLS but without all these complications? For example, Let’s Encrypt requires that you can write a file at a specific location, or the Amazon Certificate Manager needs that you put a CNAME record to the domain.

There is no central server that provides a common connection point for the clients.

#File synchronization java free#
It’s no longer a decision between trust and no trust but between a free solution and a paid one. There are hosted solutions, but using one changes the financial situation. This setup doesn’t need any trust other than the packages used.īut running and maintaining my own server is a pain. I can run my own server, use the client from third-party repositories (such as the main Ubuntu repo) and set a password. And third, the server is also available as open-source so I can install it on a machine I control.Equally important, the client is open source so that I can be reasonably sure that the encryption is implemented well.This way the server can not look into the files. First, it supports client-side encryption.This works similarly to Dropbox, but there are 3 important differences: I’ve done that, but it’s not a solution I’d recommend to anybody. Of course, you can use an encrypted filesystem (like eCryptfs) and share only that with Dropbox, but it’s a pain to configure and run. I never liked the idea that I’m sending files to a provider and only “company policy” stands in the way of it abusing them. But when there are ways to eliminate this trust they are usually more secure alternatives. You need to trust the provider, and it is the way of business in many services. And maybe not, but you can do little beyond trusting it. Maybe it does not look into your files and takes good care of security.
#File synchronization java update#
Moreover, Dropbox provides the client too, so even if it implements zero-trust encryption Dropbox can push an update to change that. The downside is that this is a machine that Dropbox controls and has access to all your files. The clients don’t need a direct way to communicate which is usually a pain due to firewalls, NATs, and dynamic IP addresses. This is a convenient setup as it relies on a central server that is globally reachable. Then if another client comes online it downloads all changed files. When one client detects a change it uploads it to the Dropbox server. Dropbox uses a central server to store your files and the clients connect to it.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
